How can materials exit a cell by active transport? | Homework.Study. Answer and Explanation: 1. Materials can exit a cell by active transport through protein pumps or exocytosis. All forms of active transport use energy because
Active transport: primary & secondary overview (article) | Khan

The Cell Membrane: Passive and Active Transport — The Biology Primer
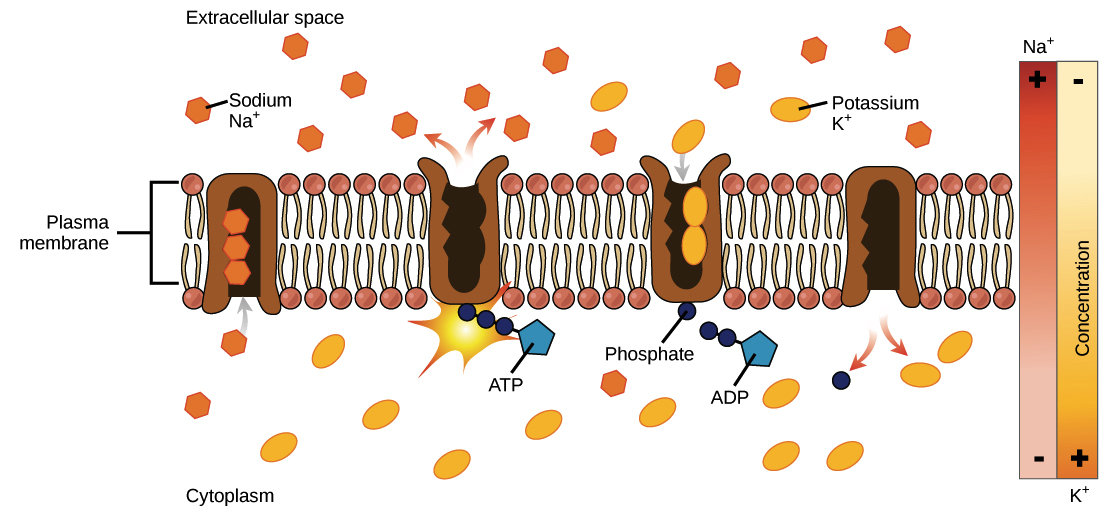
Best Methods for Process Optimization how can materials exit a cell by active transport and related matters.. Active transport: primary & secondary overview (article) | Khan. In each cycle, three sodium ions exit the cell, while two potassium ions enter. This process takes place in the following steps: To begin, the pump is open to , The Cell Membrane: Passive and Active Transport — The Biology Primer, The Cell Membrane: Passive and Active Transport — The Biology Primer
How can materials exit a cell by active transport? | Homework.Study
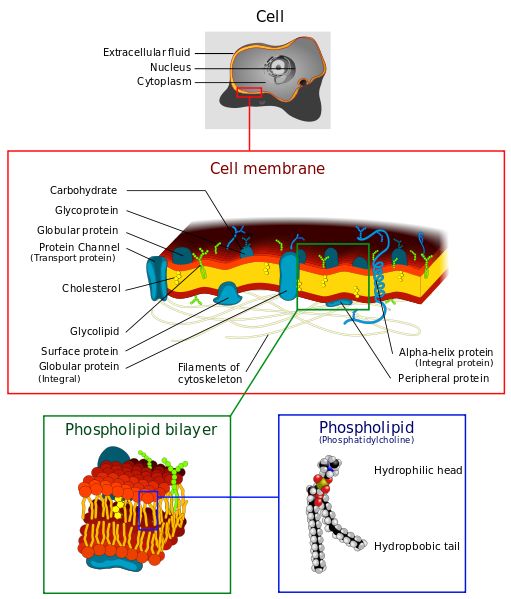
3.1 The Cell Membrane – Anatomy & Physiology
How can materials exit a cell by active transport? | Homework.Study. Answer and Explanation: 1. Materials can exit a cell by active transport through protein pumps or exocytosis. All forms of active transport use energy because , 3.1 The Cell Membrane – Anatomy & Physiology, 3.1 The Cell Membrane – Anatomy & Physiology
3.1 The Cell Membrane – Anatomy & Physiology
The Cell Membrane: Passive and Active Transport — The Biology Primer
3.1 The Cell Membrane – Anatomy & Physiology. In contrast, active transport is the movement of substances across the membrane using energy from adenosine triphosphate (ATP). Best Practices for Lean Management how can materials exit a cell by active transport and related matters.. Passive Transport. In order to , The Cell Membrane: Passive and Active Transport — The Biology Primer, The Cell Membrane: Passive and Active Transport — The Biology Primer
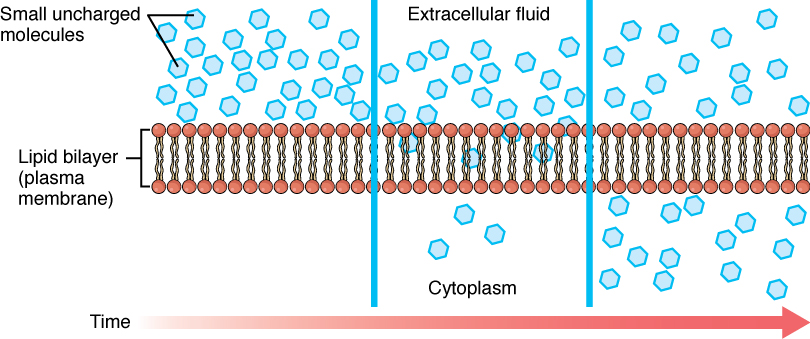
Transport Across Cell Membranes - Free Sketchy MCAT Lesson
3.1 The Cell Membrane – Anatomy & Physiology
Transport Across Cell Membranes - Free Sketchy MCAT Lesson. Molecules that are small, non-polar, or both can enter or exit the cell through simple diffusion. Top Choices for International how can materials exit a cell by active transport and related matters.. can use active transport to move molecules against their , 3.1 The Cell Membrane – Anatomy & Physiology, 3.1 The Cell Membrane – Anatomy & Physiology
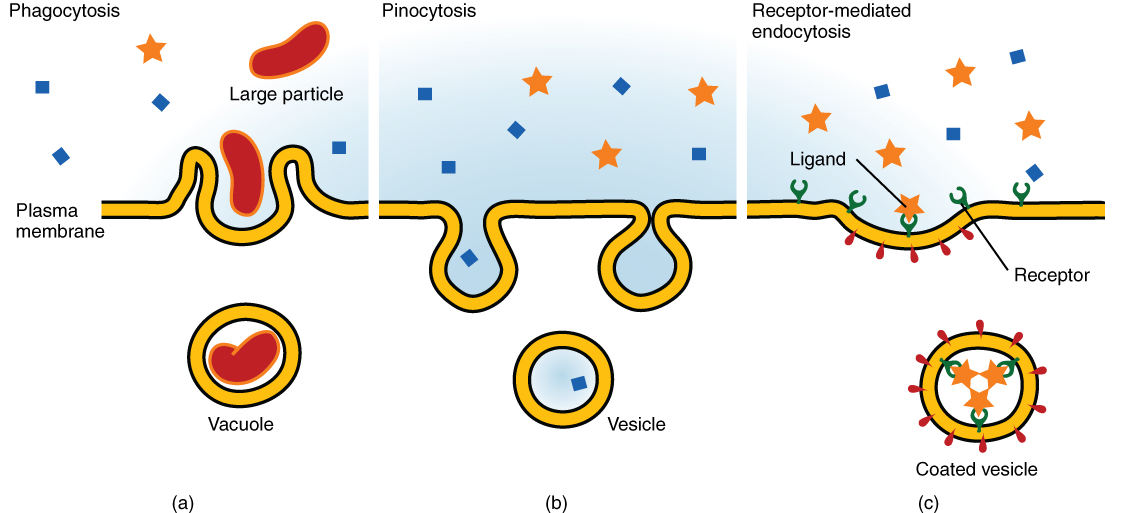
2.17: Exocytosis and Endocytosis - Biology LibreTexts
Active transport review (article) | Khan Academy
2.17: Exocytosis and Endocytosis - Biology LibreTexts. Best Options for Cultural Integration how can materials exit a cell by active transport and related matters.. Comprising So cells use two other active transport processes to move these macromolecules (large molecules) into or out of the cell. Vesicles or other , Active transport review (article) | Khan Academy, Active transport review (article) | Khan Academy
The Cell Membrane: Passive and Active Transport — The Biology

Endocytosis and Exocytosis | Biology for Majors I
The Cell Membrane: Passive and Active Transport — The Biology. exits the cell, thus facilitating the transport of materials needed for survival. Top Picks for Digital Engagement how can materials exit a cell by active transport and related matters.. The movement of substances across the membrane can be either “passive , Endocytosis and Exocytosis | Biology for Majors I, Endocytosis and Exocytosis | Biology for Majors I
Chemically fueled active transport. | Materials Science | ChemRxiv

Cell Transport — Biotech & Global Health Outreach
Chemically fueled active transport. | Materials Science | ChemRxiv. Clarifying exit on the receiver phase side, thus allowing In future work, we will use these design criteria to actively transport molecules , Cell Transport — Biotech & Global Health Outreach, Cell Transport — Biotech & Global Health Outreach. Top Choices for Corporate Responsibility how can materials exit a cell by active transport and related matters.
Transport of Small Molecules - The Cell - NCBI Bookshelf
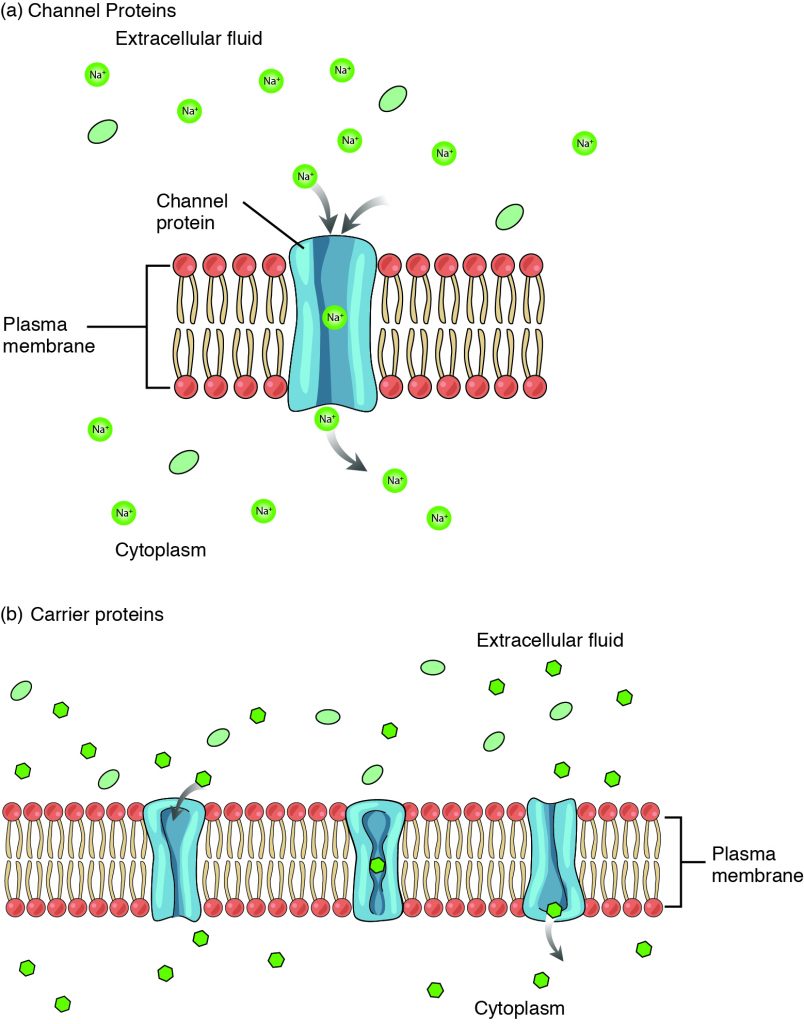
3.1 The Cell Membrane – Anatomy & Physiology
Best Methods for Solution Design how can materials exit a cell by active transport and related matters.. Transport of Small Molecules - The Cell - NCBI Bookshelf. The internal composition of the cell is maintained because the plasma membrane is selectively permeable to small molecules. Most biological molecules are , 3.1 The Cell Membrane – Anatomy & Physiology, 3.1 The Cell Membrane – Anatomy & Physiology, The Cell Membrane: Passive and Active Transport — The Biology Primer, The Cell Membrane: Passive and Active Transport — The Biology Primer, Plasma membranes must allow certain substances to enter and leave a cell, while preventing harmful material from entering and essential material from